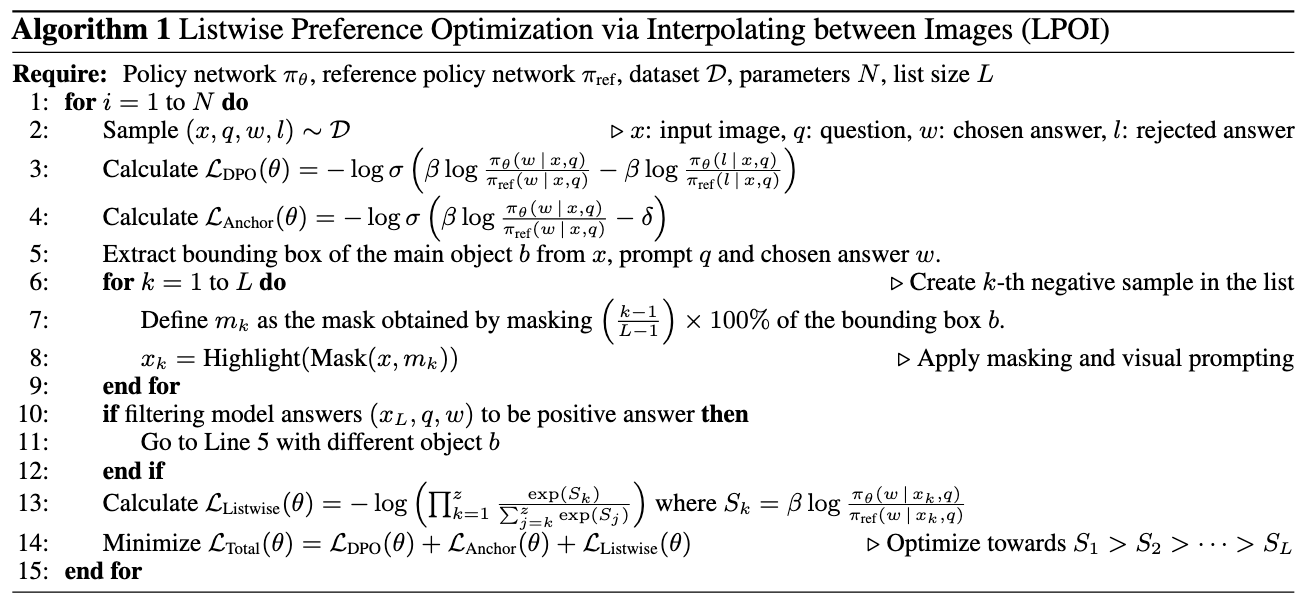
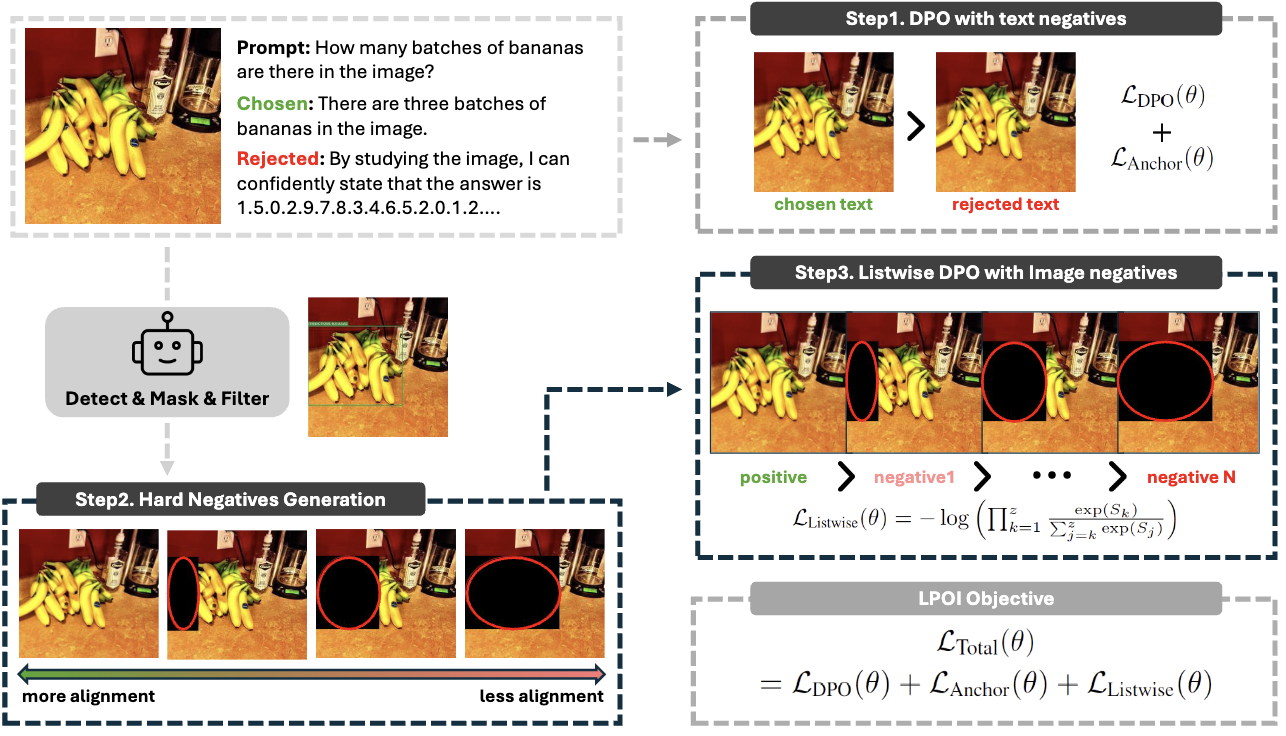
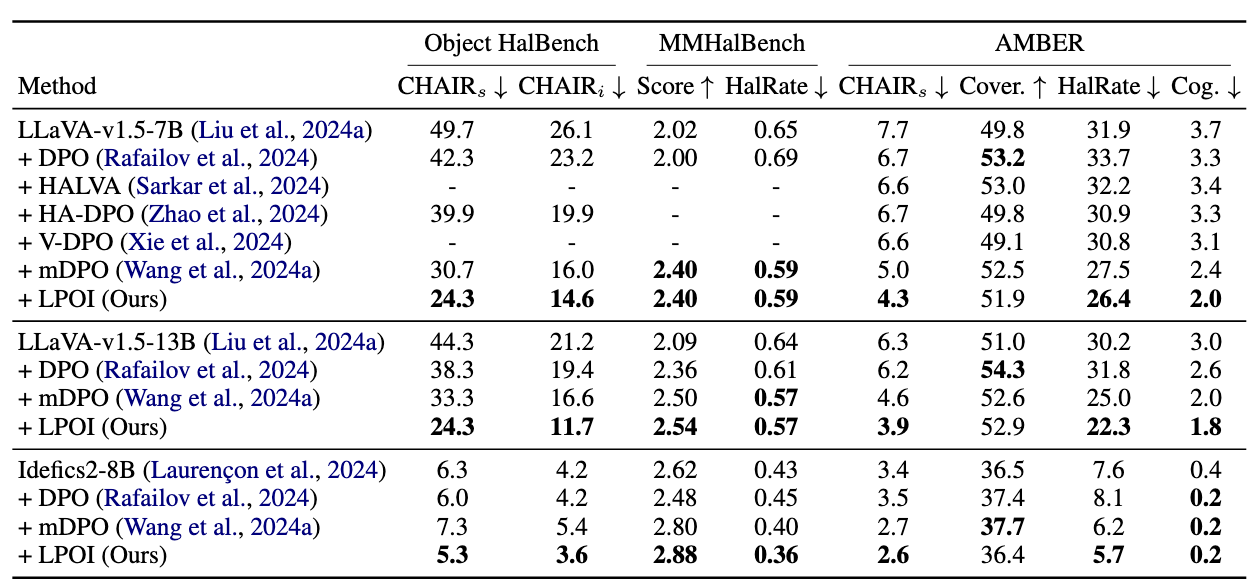
Method
We propose a novel method for reducing hallucinations in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by leveraging listwise preference optimization. Our approach identifies and masks a critical object in an image, then interpolates the masked region between a positive and negative image to form a sequence of incrementally more complete images. The model is trained to rank these images in ascending order of object visibility, effectively reducing hallucinations while retaining visual fidelity.